Pytorch基础
本篇是对Pytorch基础使用的学习,主要基于B站小土堆的https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1hE411t7RN/以及Gemini的帮助,除实践外也包含了一些深度学习模型的原理
Dataset
An abstract class representing a Dataset.
All datasets that represent a map from keys to data samples should subclass it. All subclasses should overwrite __getitem__, supporting fetching a data sample for a given key. Subclasses could also optionally overwrite __len__, which is expected to return the size of the dataset by many ~torch.utils.data.Sampler implementations and the default options of ~torch.utils.data.DataLoader. Subclasses could also optionally implement __getitems__, for speedup batched samples loading. This method accepts list of indices of samples of batch and returns list of samples.
note
~torch.utils.data.DataLoaderby default constructs an index sampler that yields integral indices. To make it work with a map-style dataset with non-integral indices/keys, a custom sampler must be provided.
一个表示数据集的抽象类。
所有实现从键(keys)到数据样本(data samples)映射的数据集都应该继承这个类。所有子类都必须重写
__getitem__方法,以支持根据给定的键获取数据样本。子类也可以选择性地重写__len__方法,许多~torch.utils.data.Sampler实现和~torch.utils.data.DataLoader的默认选项都需要通过这个方法返回数据集的大小。子类还可以选择性地实现__getitems__方法,以加速批量样本的加载。此方法接受批处理样本的索引列表,并返回样本列表。注意
默认情况下,
~torch.utils.data.DataLoader会构造一个生成整数索引的采样器。要让其与非整数索引/键的映射式数据集一起工作,必须提供自定义的采样器。
自定义Dataset
那么在实际的使用中,比如有一个数据集(我们拿之前用过的fer2013来举例):
-
先定义一个数据类继承
Dataset,定义__init__()from torch.utils.data import Dataset
import os
class MyData(Dataset):
def __init__(self, root_dir, label_dir):
self.root_dir = root_dir # 如 fer2013/test
self.label_dir = label_dir # 如 angry
self.path = os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.label_dir) # 路径合并函数 解决跨系统的文件路径问题
self.img_path = os.listdir(self.path) # 如angry文件夹下,所有图片名的string list -
重写
__getitem()def __getitem__(self, index):
img_name = self.img_path[index]
img_item_path = os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.label_dir, img_name) # 拼接出具体的某一个图片的路径
img = Image.open(img_item_path)
label = self.label_dir
return img, label # 返回数据集中的一个对象(图片)及其类型 -
重写
__len()__def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_path) -
定义示例
root_dir = "fer2013/train"
angry_label_dir = "angry"
angry_dataset = MyData(root_dir, angry_label_dir) -
Dataset合并
disguest_label_dir = "disguest"
disgust_dataset = MyData(root_dir, disguest_label_dir)
train_dataset = angry_dataset + disgust_dataset # '+'
TensorBoard
SummaryWriter
- 创建日志目录
- 初始化
Writer对象 - 生成事件文件
- 这个文件才是真正的数据库(events.out…)当后续调用
writer.add_scalar时,数据并不是直接画在屏幕上,而是被追加写进这个文件里。 - 当你执行完相应代码,运行
tensorboard --logdir=logs时,TensorBoard 的后端服务器就会去读取这个文件里的内容,并在浏览器里渲染成图表。
- 这个文件才是真正的数据库(events.out…)当后续调用
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter |
需注意,每次实验可以用不同的文件夹来记录数据,比如writer = SummaryWriter("logs/lr0.01_batch32")修改了学习率后writer = SummaryWriter("logs/lr0.001_batch32")
add_scalar()
- 绘图函数
add_scalar()
(method) def add_scalar( |
add_image()
- 查看图片函数
add_image()
(method) def add_image( |
要注意参数的类型要求:img_tensor (torch.Tensor, numpy.ndarray, or string/blobname): Image data,所以要将PIL类型的图片进行转换,比如用numpy来转换。以及数据的shape要求: Tensor with :math:(1, H, W), :math:(H, W), :math:(H, W, 3) is also suitable as long as corresponding dataformats argument is passed, e.g. CHW, HWC, HW. 即三种图片数据的格式,其通道数、高度、宽度的顺序不同。
img = Image.open(image_path) |
add_graph()
常见的Transforms
下面基本都是对图像的处理方法
ToTensor
Convert a PIL Image or ndarray to tensor and scale the values accordingly.
This transform does not support torchscript.
Converts a PIL Image or numpy.ndarray (H x W x C) in the range [0, 255] to a torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) in the range [0.0, 1.0] if the PIL Image belongs to one of the modes (L, LA, P, I, F, RGB, YCbCr, RGBA, CMYK, 1) or if the numpy.ndarray has dtype = np.uint8
In the other cases, tensors are returned without scaling.
note
-
Because the input image is scaled to [0.0, 1.0], this transformation should not be used when transforming target image masks. See the [references](vscode-file://vscode-app/d:/Microsoft VS Code/resources/app/out/vs/code/electron-browser/workbench/workbench.html) for implementing the transforms for image masks.
-
将PIL图片转为torch类型,如
torch.Size([1, 48, 48])
trans_totensor = transforms.ToTensor() |
Normalize
Normalize a tensor image with mean and standard deviation.
This transform does not support PIL Image.
Given mean: (mean[1],...,mean[n]) and std: (std[1],..,std[n]) for n
channels, this transform will normalize each channel of the input
torch.*Tensor i.e.,
output[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]
note:
This transform acts out of place, i.e., it does not mutate the input tensor.
Args:
mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
inplace(bool,optional): Bool to make this operation in-place.
Normailize的数学原理是:
- 参数
mean影响的是“中心位置”,在ToTensor之后,像素值在 之间,中心大约在 ,如mean = 0.5,那么减去 后,数据的中心变成了 。原本 的范围变成了 - 参数
std影响的是“缩放幅度”,如std = 0.5,那么就是将数据范围再除以,最终范围从 变成了
Resize
Resize the input image to the given size.
If the image is torch Tensor, it is expected
to have […, H, W] shape, where … means a maximum of two leading dimensions
Args:
size (sequence or int): Desired output size. If size is a sequence like
(h, w), output size will be matched to this. If size is an int,
smaller edge of the image will be matched to this number.
i.e, if height > width, then image will be rescaled to
(size * height / width, size).
resize()支持PIL和Tensor两种图片格式,如果是 Tensor,期望形状为[..., H, W]。这里的...表示它可以处理[C, H, W](单张图)或[B, C, H, W](一个 Batch 的图)- 参数
size需注意写成序列形式,如resize((512, 512)),而如果只输入一个参数,如resize(512),那么图片短边会变为512,而长边会按比例改变
print(img.size) |
Compse
Composes several transforms together. This transform does not support torchscript.
Please, see the note below.
Args:
transforms (list of Transform objects): list of transforms to compose.
compse()操作是对各种transforms操作的流水线类- 在深度学习中,图片通常需要经过一系列的固定步骤(比如:缩放 -> 转为 Tensor -> 归一化)。如果不用
Compose,你每一张图都要手动调用多个函数,代码会非常冗余 compse()的参数类型是一个列表,操作是按顺序执行的,所以前一个操作输出的数据类型必须能作为下一个操作的输入。
from torchvision import transforms |
Pytorch数据集使用
例如,我们要导入视觉学习的数据集,可以直接在程序中进行数据集的下载
import torchvision |
root参数表示数据集存放的位置,train参数表示数据集是否用来训练,download参数表示是否下载到本地(会生成一个下载链接)- 具体的参数设置,每个数据集都可能有所区别…
- 如果是下载完成到本地的数据集,可以将其复制到项目目录的dataset文件夹下,再运行程序即可节省下载的时间
print(test_set.classes) # 可以看到测试数据集的所有类别 |
DataLoader
Data loader combines a dataset and a sampler, and provides an iterable over the given dataset.
The :class:~torch.utils.data.DataLoader supports both map-style and
iterable-style datasets with single- or multi-process loading, customizing
loading order and optional automatic batching (collation) and memory pinning.
在训练模型时,不能一次性把数据集中的大量数据塞进内存。DataLoader实现了:
- Batching(批处理): 把图片打包成一组组(Batch)。
- Shuffling(打乱): 每一轮训练(Epoch)开始时随机洗牌,防止模型死记硬背数据顺序。
- Parallel Computing(并行加载): 利用多核 CPU 提前准备下一批数据,不让 GPU 等待。
| 参数名 | 常用取值 | 作用描述 |
|---|---|---|
| dataset | 自定义 Dataset | 必填。告诉 DataLoader 从哪个“仓库”取数据。 |
| batch_size | 16, 32, 64… | 每批装载的数量。 越大训练越快,但越占显存。在 FER 表情识别中,32 或 64 是常用数值。 |
| shuffle | True / False |
是否打乱顺序。 训练集通常设为 True(增加随机性);测试集通常设为 False。 |
| num_workers | 0, 2, 4, 8… | 多进程加载。 0 表示只用主进程(慢)。增加数值可以加快读取速度。建议: 设为 CPU 核心数的一半。 |
| drop_last | True / False |
丢弃最后多余的数据。 比如有 100 张图,batch_size=32。最后剩 4 张不够一包,设为 True 就会把这 4 张扔掉,确保每个 Batch 大小一致。 |
| pin_memory | True |
内存锁页。 如果你用 GPU 训练,设为 True 可以加快数据从内存传输到显存的速度。 |
- 例如,我们用
DataLoader处理CIFAR10中的数据
test_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("./dataset", train=False, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), download=True) |
- 结合循环和
tensorboard,输出每一个epoch中每一step用到的图片 - 下面代码中
step + epoch * len(test_loader)是使用了全局步长,也可以不这样写,而是把每个epoch来当作一组
writer = SummaryWriter("dataloader") |
nn.Module
Base class for all neural network modules.
Your models should also subclass this class.
Modules can also contain other Modules, allowing to nest them in a tree structure.
- 在 PyTorch 中,无论是简单的线性层,还是复杂的 VGG16 或 Transformer,本质上都是一个
nn.Module。它是所有神经网络模块的基类 nn.Module支持嵌套,当你对大模型调用model.to("cuda")时,PyTorch 会顺着这棵“树”,自动把里面所有的子层都搬到 GPU 上。- 只要在
__init__中把一个层赋值给self.xxx,PyTorch 就会自动识别出其中的权重 (Weights) 和 偏置 (Bias),并将它们加入到待优化的参数列表中。
编写一个nn.Module子类时,必须重写__init()__和forward()
__init(self)__- 在这里定义网络层(卷积、池化、全连接等)。
- 必须调用
super().__init__()。这行代码的作用是初始化父类的属性,如果没有它,PyTorch 就没法自动追踪定义的层,模型也就无法训练。
forward(self, x)- 定义数据的流向。图片进去后,先过哪一层,再过哪一层。
- 不需要手动调用
forward,只需要运行model(input),PyTorch 会自动触发forward。
import torch |
卷积 Conv
| 参数 | 含义 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| in_channels | 输入通道数 | 彩色图通常为 3 (RGB),灰度图为 1。 |
| out_channels | 输出通道数 | 卷积核的数量。有多少个核,输出就有多少层特征图。 |
| kernel_size | 卷积核大小 | 提取特征的“窗口”大小。常用 3 或 5(VGG 常用 3)。 |
| stride | 步长 | 窗口滑动的跨度。默认为 1。步长越大,输出图片越小。 |
| padding | 填充 | 在图片四周补 0。'same' 保持大小不变,'valid' 则不补。 |
| dilation | 空洞卷积 | 卷积核点之间的间距。用于扩大感受野(不用增加参数量)。 |
| bias | 偏置 | 是否在结果上加一个常数偏移。默认开启。 |
- 卷积的Padding(边界扩充)参数很重要,如果周围不补零,那么卷积会导致图像尺寸越来越小
- 形状计算公式:
H_{out} = \left\lfloor\frac{H_{in} + 2 \times \text{padding}[0] - \text{dilation}[0] \times (\text{kernel_size}[0] - 1) - 1}{\text{stride}[0]} + 1\right\rfloor
计算同理
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("./dataset",train = False, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),download=True) |
step = 0 |
(最大)池化 MaxPool
- 最大池化的逻辑非常简单:在一个窗口(Kernel)范围内,只保留最大的那个值,剩下的全部扔掉
- 既保留输入特征,又减小了数据量,加快训练速度
| 参数 | 独特之处 |
|---|---|
| kernel_size | 窗口大小。常见是 2(即将 的区域合并)。 |
| stride | 默认值等于 kernel_size!这和卷积不同。如果 kernel_size=2,步长默认就是 2,这样窗口之间就不会重叠。 |
| ceil_mode | 非常重要。 默认是 False(向下取整)。如果设为 True(向上取整),当窗口超出边界时,只要窗口内有数据,就会保留结果,而不是舍弃。 |
| padding | 填充。注意池化填充的是负无穷(),这样是为了保证填充位不会被选为最大值。 |
input = torch.tensor([[1,2,0,3,1], |
torch.Size([1, 1, 5, 5]) |
损失函数与反向传播
- 损失函数用于计算实际输出与目标之间的差距,为反向传播、更新参数提供一定的依据。在分类任务中,常用交叉熵函数来计算误差,
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() |
优化器
torch.optim — PyTorch 2.10 documentation
- 示例代码:
for input, target in dataset: |
Pytorch实战:CIFAR10
- 针对CIFAR10图像数据集的简单分类模型实战
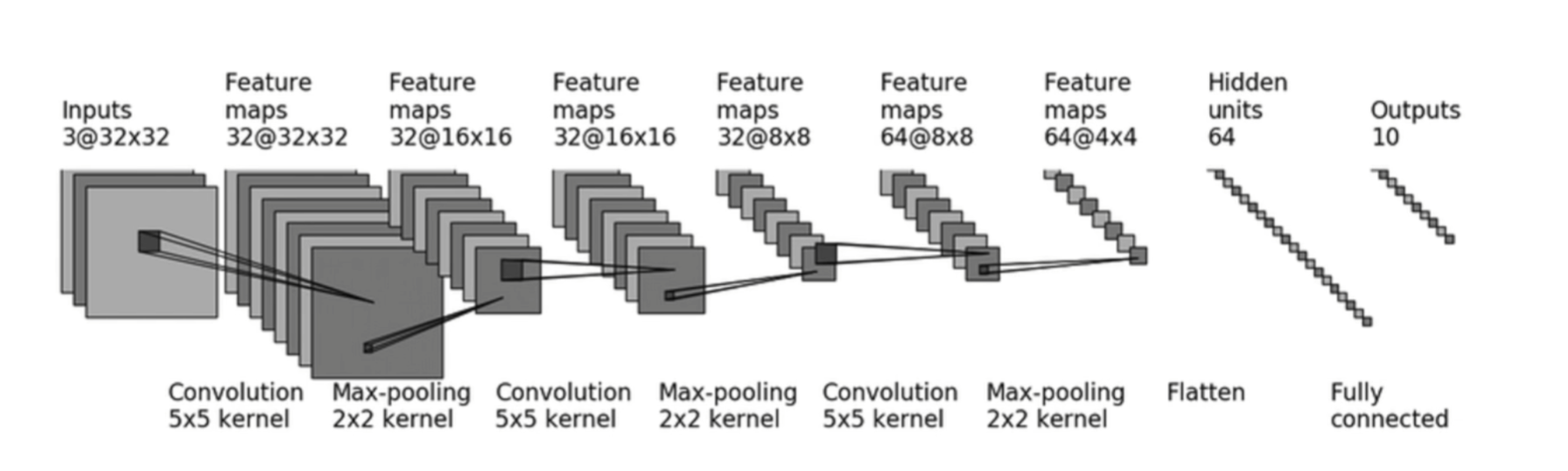
- 首先了解Sequential,
nn.Sequential是nn.Module的一个特殊子类,它的作用是自动完成forward逻辑。注意:其中每一个参数都是某层的类,所以要写逗号。Sequential既简化了模型定义,也简化了forward()。
class CIFAR10_Simple(nn.Module): |
-
在搭建模型前,先设置
DataLoader处理数据集- 分别设置好
train_data和test_data
- 分别设置好
dataset_transfrom = tf.Compose([tf.ToTensor(),tf.Normalize((0.5,0.5,0.5),(0.5,0.5,0.5))]) |
- 搭建好模型后,简单测试输出尺寸是否符合要求
cifar = CIFAR10_Simple() |
- 训练前的基本设置
- 定义
TensorBoard的writer - 设置
device调用显卡加速训练 - 实例化训练模型
- 定义损失函数
- 设置优化器
- 定义
writer = SummaryWriter("./logs") |
- 训练部分
- 优化器的定式代码
- 记录训练损失
total_step = 0 |
- 评估部分
- 每个epoch执行一次
with torch.no_grad():关闭梯度记录- 统计性能指标
model.eval() |
- 可视化
# 输出到 TensorBoard |